Blog
Dental hygiene tips for healthy teeth & gums
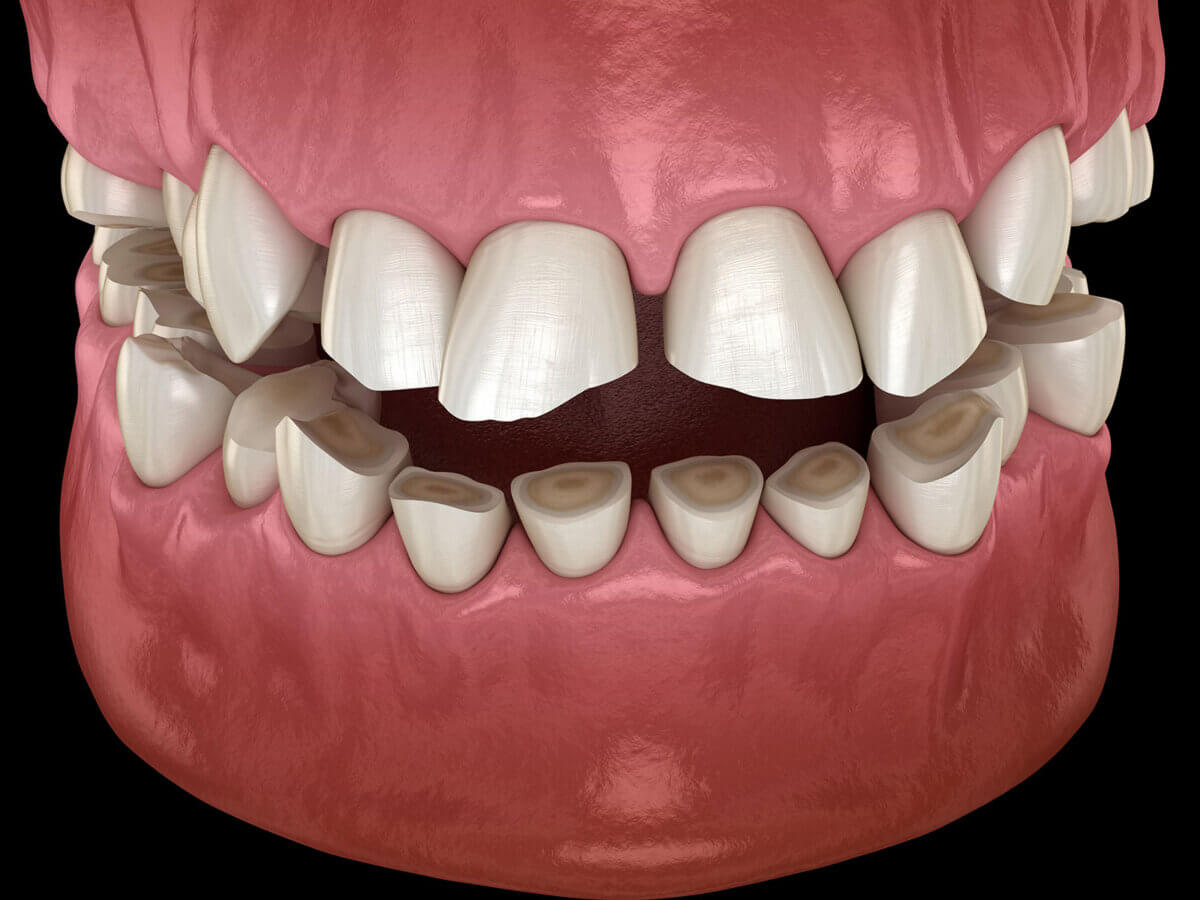
What Can I Do To Prevent Dental Erosion?
Dental erosion, often referred to as tooth erosion, is the loss of mineralized tooth substance due to acid exposure. This condition can lead to the dissolution of dental hard tissue if not addressed promptly. Common causes include acidic foods, drinks, or medications. Additionally, conditions like vomiting or acid reflux can contribute to tooth erosion.
It’s essential to differentiate between dental erosion and tooth decay. While bacteria cause tooth decay, dental erosion involves the wearing away of the tooth’s outer hard layer. This article will delve into the nature of tooth erosion and how to prevent it.
What is Dental Erosion?
Dental erosion occurs when acid dissolves a portion or the entire tooth surface. This condition can manifest at any age and can significantly compromise oral health. Major contributors to dental erosion include a decrease in saliva production due to aging, acid reflux, or frequent vomiting.
Elderly individuals often experience dry mouths, leading to tooth erosion due to reduced saliva production. Such conditions necessitate immediate attention from dental professionals.
Symptoms Of Dental Erosion
Eroded teeth typically appear chalky or pitted. They may also exhibit a yellow, pale, or discolored hue. The edges of eroded teeth tend to be sharp, leading to heightened sensitivity. Such teeth react strongly to hot, cold, sugary, or acidic foods. As erosion progresses, teeth become increasingly susceptible to decay and other infections.
Tooth erosion is a gradual process, but its rate can accelerate over time. The underlying layers of teeth are sensitive and can become irritated or inflamed upon contact with acidic substances. Taking preventive measures can mitigate the adverse effects of erosion.
Causes of Enamel Erosion
Dental erosion can arise from both external and internal factors. External causes encompass diet, medications, and one’s daily environment. Consuming excessive amounts of acidic or sugary drinks can damage teeth and lead to erosion. Additionally, foods containing citric or phosphoric acids can be detrimental to dental health.
Internally, certain health conditions can precipitate tooth erosion. For instance, older adults often experience dry mouths, leading to reduced saliva production and subsequent erosion. Disorders like bulimia, gastric reflux, alcoholism, and frequent vomiting can also render the oral environment acidic.
Treatment and Preventions
Untreated dental erosion can result in significant loss of tooth structure. Dentists typically address this issue using veneers, fillings, crowns, root canal treatments, or tooth extractions. They may also apply fluoride varnish and recommend a comprehensive management plan to halt further erosion.
The most effective preventive measure against erosion is to limit the intake of sugary drinks and acidic substances. Reducing the consumption of tea, coffee, and other caffeinated products, coupled with rinsing the mouth with water, can also help. Excessive alcohol consumption can exacerbate erosion and accelerate tooth dissolution.
Final Thoughts
Several factors, both internal and external, contribute to dental erosion. Maintaining a dental routine that minimizes sugar and acid intake is crucial for preserving tooth health and reducing erosion risk. If an underlying condition is causing enamel dissolution, it’s essential to consult a dentist for guidance.
In addition to personal dental hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups are vital for maintaining healthy teeth and gums. While prevention is always the best approach, any emerging dental issues should be addressed promptly.
Adhering to a dentist’s recommendations and planning your routine accordingly can ensure timely and effective treatment, safeguarding your teeth from further damage.


